Table of Content
Try Vizitor for Free!
Thu, Feb 6, 2025
Read in 9 minutes
The way businesses operate is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and the need for greater efficiency. Automation is at the center of this transformation, allowing organizations to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and reduce costs. As workplaces grow more complex, automation has become an essential tool for improving overall efficiency and ensuring seamless business operations.
1. Understanding Workplace Automation
What is Workplace Automation?
Workplace automation refers to the use of technology to streamline repetitive and administrative tasks, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency. This can involve anything from automating emails and data entry to advanced AI-driven decision-making systems that help businesses make data-backed choices.
Automation is not just about replacing human workers—it is about optimizing processes, improving accuracy, and allowing employees to focus on high-value tasks.
For instance, have you ever found yourself spending hours copying and pasting data, manually scheduling meetings, or processing invoices? These are exactly the types of tasks that automation can handle.

The Need for Automation in Business
Businesses today face increasing demands for speed, accuracy, and scalability. Relying on traditional, manual processes often results in inefficiencies, human errors, and increased operational costs. Automation helps eliminate these challenges by allowing companies to handle repetitive tasks more effectively, freeing up employees to focus on higher-value work.
Moreover, workplace automation plays a crucial role in ensuring security, maintaining compliance, and enhancing user experiences. As businesses expand, the volume of daily tasks—ranging from managing resources to processing information—continues to grow. Without automation, these tasks can become overwhelming and time-consuming.
How Automation is Transforming Business Operations
Automation is changing the way businesses function in several ways:
- Increased Efficiency – Automating routine tasks saves time and reduces human intervention, leading to faster and more consistent results.
- Cost Reduction – By optimizing workflows and minimizing manual labor, businesses can significantly cut operational expenses.
- Enhanced Accuracy – Human errors in data entry, scheduling, and communication can be costly. Automation ensures greater precision in everyday operations.
- Better Resource Utilization – Automation helps businesses allocate resources more effectively, reducing waste and improving productivity.
- Improved Decision-Making – Data-driven automation provides valuable insights that help businesses make informed decisions and respond to market changes efficiently.
Why Businesses Must Embrace Automation
The modern workplace is no longer static—it is dynamic, fast-moving, and highly competitive. Businesses that fail to adapt to automation risk inefficiencies, increased costs, and decreased customer satisfaction. Automation is not just about replacing manual tasks but about creating a more structured, intelligent, and future-ready workplace.
With advancements in technology, the role of automation will continue to expand. Organizations that recognize the value of automation and integrate it into their operations will gain a competitive edge, improve their service delivery, and build a more resilient business for the future.
In an era where time, efficiency, and precision are critical, automation is no longer an option—it is a necessity for long-term business success.
2. Benefits of Automation in the Workplace
Businesses that embrace automation can expect improved efficiency, lower operational costs, and better customer experiences. Here are some key benefits:

1. Increased Productivity
Automation speeds up processes that would otherwise take employees hours to complete manually. This means faster task completion and more time for strategic initiatives.
2. Improved Accuracy
Unlike human workers, automated systems do not get tired or distracted, ensuring fewer errors in data entry, financial calculations, and record-keeping.
3. Cost Savings
By reducing the need for manual labor in repetitive tasks, automation helps companies save on operational costs while improving efficiency.
4. Employee Satisfaction and Well-being
Employees spend less time on tedious tasks, leading to higher job satisfaction, reduced stress levels, and greater motivation to focus on innovation and problem-solving.
5. Enhanced Customer Experience
Automation improves response times, service accuracy, and overall customer engagement. For example, automated chatbots provide instant customer support, ensuring users get the help they need without long wait times.
6. Data-Driven Decision Making
Automation allows businesses to collect and analyze real-time data, providing valuable insights for making more informed business decisions.
3. The Need for Workplace Automation
In today’s fast-paced economy, businesses must keep up with increasing competition, customer expectations, and digital transformation. The demand for faster, error-free processes has made automation a necessity rather than an option.
Why Businesses Can No Longer Ignore Automation
- Manual processes slow down operations, leading to missed deadlines and inefficiencies.
- High labor costs make businesses less competitive.
- Employees spend valuable time on tasks that can be easily automated.
- Customers expect fast, personalized, and seamless experiences.
By integrating automation, businesses can focus on strategic growth instead of administrative bottlenecks.
4. Challenges Businesses Face Without Automation
Businesses that hesitate to adopt automation face several key challenges, particularly in visitor management, customer relationship management (CRM), human resources (HR), and queue management systems. Without automation, these areas become prone to inefficiencies, errors, and operational bottlenecks.
- Inefficient Operations
Manual processes in visitor management systems (VMS) lead to long wait times, security risks, and difficulty in tracking visitor history. Similarly, without automated CRM solutions like Leadhooper, businesses struggle to track and manage leads efficiently, often missing valuable sales opportunities. - Human Errors and Data Inconsistencies
Manual HR systems make attendance tracking, payroll processing, and employee management prone to errors, leading to compliance issues and payroll disputes. Automating attendance management ensures accurate records, reducing discrepancies and administrative overhead. - High Operational Costs
Labor-intensive processes such as managing queues manually for e-ticketing systems result in unnecessary staffing costs. Automated queue management optimizes resource allocation, reducing workforce dependency while improving service delivery. - Employee Burnout and Dissatisfaction
Repetitive tasks in HR, sales, and customer service leave employees frustrated and disengaged. Automating mundane administrative tasks frees up employees for more meaningful, strategic work. - Poor Customer Experience
Slow response times, lack of personalization, and inefficient service delivery lead to dissatisfied customers. Automated customer relationship management (CRM) and AI-powered queue management systems for e-ticketing enhance customer interactions and streamline service processes.
5. Examples of Workplace Automation
Automation is transforming various aspects of business operations, from customer engagement to workforce management.
1. Marketing & Sales
- AI-driven CRM systems (e.g., Leadhooper) optimize lead generation, follow-ups, and customer segmentation.
- Automated email marketing campaigns increase engagement and conversion rates.
- Chatbots handle customer inquiries, providing instant responses and reducing workload.
2. Human Resources
- Automated attendance management systems accurately track work hours, reducing payroll errors.
- Resume screening and applicant tracking streamline the hiring process.
- Digital onboarding systems reduce paperwork and speed up employee integration.
3. Finance & Accounting
- Automated invoicing and payment processing reduce human error.
- AI-driven fraud detection systems identify suspicious activities in real-time.
4. Customer Service
- Self-service portals and automated ticketing systems for queue management reduce customer wait times.
- AI chatbots enhance response times and personalize customer interactions.
5. Operations & Administration
- Automated visitor management systems (VMS) streamline guest check-ins, ensuring security compliance.
- Real-time inventory tracking reduces stock shortages and improves supply chain efficiency.
- Workflow automation for approvals and document management enhances internal collaboration.
Automation is not just for large enterprises; small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) can also benefit by integrating these technologies into daily operations.
6. Future of Automation in the Workplace
The future of workplace automation is driven by AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA). Businesses that embrace these trends will stay ahead in an increasingly digital landscape.
1. AI and Machine Learning
- AI-powered predictive analytics help optimize visitor traffic, sales forecasting, and HR management.
- Machine learning improves CRM automation, ensuring businesses engage with the right customers at the right time.
2. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- Automating repetitive data entry, customer inquiries, and queue management reduces human workload.
- RPA tools will streamline financial transactions, expense reporting, and compliance documentation.
3. Cognitive Automation
- AI-powered systems will analyze contracts, compliance records, and HR policies, reducing legal risks.
- Smart automation tools will manage workflows across multiple departments.
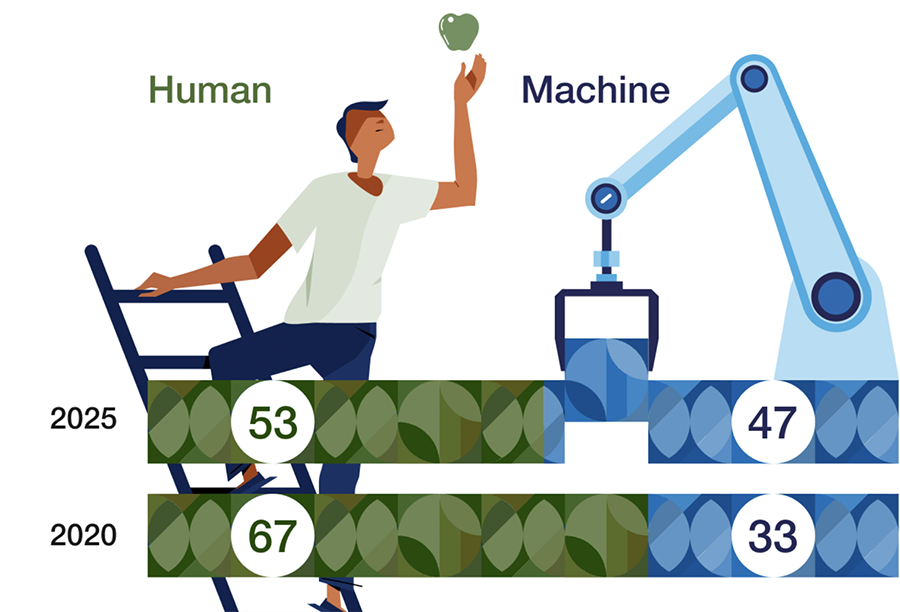
4. Human-Machine Collaboration
Rather than replacing jobs, automation will enable employees to work alongside intelligent systems, enhancing productivity and decision-making.
Companies investing in AI-driven queue management, CRM automation, and HR tech solutions will gain a competitive edge in efficiency and customer satisfaction.
7. Conclusion
Workplace automation is no longer an option—it is a necessity for businesses seeking growth, efficiency, and improved customer and employee experiences.
By adopting automation in key areas such as:
Visitor Management – Faster check-ins, improved security, and real-time visitor tracking.
CRM Solutions (e.g., Leadhooper) – Smarter lead management, personalized customer interactions, and higher conversion rates.
HR & Attendance Management – Accurate payroll, reduced manual errors, and streamlined onboarding.
Queue Management for E-Ticketing – Reduced wait times, improved customer service, and better resource allocation.
Automation enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and allows businesses to focus on strategic initiatives rather than repetitive tasks. Companies that integrate smart automation today will be well-positioned for long-term success in a technology-driven economy.
8. Frequently Asked Questions
8.1. Will automation replace jobs, or will it create new opportunities?
Automation is designed to enhance efficiency by eliminating repetitive tasks, not replace human workers entirely. While certain roles may evolve or shift, automation creates opportunities for upskilling, innovation, and higher-value work.
8.2. What skills will be most valuable in an automated workplace?
As automation takes over routine processes, employees will need to focus on skills that require human intelligence and creativity, such as:
- Data analysis & AI literacy – Understanding how automation and AI work.
- Problem-solving & critical thinking – Managing complex, non-automatable challenges.
- Emotional intelligence & leadership – Handling teamwork, decision-making, and strategic planning.
8.3. How can employees and businesses prepare for the future of automation?
Both individuals and organizations can take proactive steps to stay ahead of workplace automation:
- Employees should focus on acquiring digital skills, learning about AI applications, and staying informed about industry trends.
- Businesses should invest in workforce training programs, ensuring employees can transition into higher-value roles.
8.4. What ethical concerns does automation raise, and how can they be addressed?
The adoption of automation comes with ethical responsibilities, including:
- Job displacement – Companies must implement workforce transition programs.
- Data privacy – Protecting user information while leveraging AI-driven automation.
- Bias in AI – Ensuring automation tools are programmed without discriminatory biases.
8.5. How can businesses implement automation effectively for maximum impact?
To ensure successful automation integration, businesses should:
- Start with high-impact areas like CRM, visitor management, HR automation, and queue management systems to see immediate efficiency gains.
- Prioritize employee training so that teams can adapt to automation rather than resist it.
- Continuously evaluate and optimize automation processes to ensure they align with evolving business needs.









